Methods of Abortion
It is very important, that in every abortion, all the unborn child and the placenta is removed to prevent the risk of abortion. The placenta is an organ that connects the developing foetus to the wall of the uterus. This allows important processes via the mother's body, e.g. Nutrient Uptake, Waste Elimination and Gas Exchange.
-
Surgical Abortion
Surgical Abortion is the physical method used to remove the foetus from the uterus. A Surgical Abortion is done under General or Local Anaesthetic.
Suction Aspiration:
This method of surgical abortion is most common within the first trimester (first 12 weeks) of pregnancy. The cervix is forced open where a canula (hollow tube with knife-edge tip) is inserted into the womb. The canula is attached to a powerful vacuum which sucks the foetus down in pieces. If the head is too large, it must be smashed and crushed in order to be removed
Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
This method of abortion is also common within the first trimester of pregnancy. The cervix is forced open where a curette or scraping instrument is used to scrape the unborn child out.

Dilation and Evacuation (D&E)
This method of surgical abortion is used after the first trimester of pregnancy. In this method, small forceps are used to crush and dismember the body and crush the unborn child's head before removal.
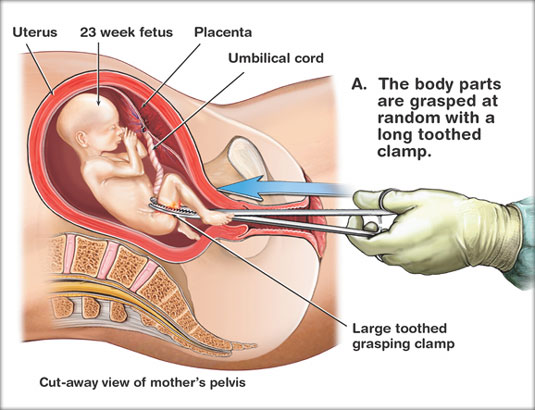
Dilation and Extraction (D&X)
This method of abortion is rare and is only used after the 20-week mark. It can also be called the Partial-Birth method.The cervix is forced open where the unborn child is drawn from the birth-canal until only the head is delivered. From there, a sharp instrument is stabbed into the centre of the head and sucks the contents of the skull out. The deceased and limp body is then evacuated from the womb.
-
Medical Abortion
A medical abortion is a common method of abortion when the person who needs an abortion does not want a surgery. A medical abortion involves using drugs such as prostaglandins, mifepristone, methotrexate to induce intense labour. From there, the child is expelled from the womb. In certain situations, the foetus may be delivered alive but is usually left to die or poisoned before birth.